What Is A Good Operating Expense Ratio For A Hvac Service Co
Understanding how much coin information technology takes to keep a company running is critical to the viability of all organizations. Every bit operating expenditures increase, profitability decreases. Therefore, by beingness enlightened of and proactively mitigating the toll of operations, businesses have the potential to meliorate control costs and improve their financial health.
What Are Operating Expenses?
Operating costs are expenditures directly related to day-to-mean solar day concern activities, excluding the processes involved in manufacturing a product or delivering a service. Examples include hire, travel, utilities, salaries, office supplies, maintenance and repairs, property taxes and depreciation (see beneath for a more comprehensive listing).
Operating vs. Non-Operating Expenses
A company's operating expenses, sometimes called OpEx, are reflected in its income statement. Along with non-operating expenses, they help businesses calculate their profitability. Non-OpEx are expenditures indirectly related to operations that are the result of financing or investing activities, like interest payments on loans.
Operating (and not-operating) expenses can be fixed — unaffected by changes in production volume or service delivery — or variable, pregnant they fluctuate in proportion to the changes in volume or delivery. While hire and salaries are examples of fixed OpEx, fuel and sales commissions are variable ones.
Operating Expenses vs. COGS
Operating expenses are dissimilar from the cost of goods sold (COGS), which are the direct expenses a business concern pays to buy or manufacture its products. COGS can be difficult to summate depending on the complication of the business concern and what it sells. In the simplest of terms, COGS include the beginning inventory plus inventory purchases minus the ending inventory. This formula includes the cost of purchasing the items, entering freight, manufacturing (including labor), modification and packaging.
Capital Expenses vs. Operating Expenses
Unlike COGS and OpEx, capital expenses practice not prove up on the company's income statement. Capital expenses, or CapEx, are i-time expenditures of tangible or nontangible avails that are reflected on a visitor'south balance canvas. These avails normally have a lifespan of one yr or more and bring longer-term value to the business.
While upper-case letter expenditures are deductible, the deduction occurs over a menstruation of fourth dimension, rather than immediately. Those deductions happen through processes called depreciation and amortization. Note: In some cases, for sure nugget categories, 100% first-yr depreciation is immune.
Fundamental Takeaways
- Every organization has operating expenses that come with running a business organization and make information technology possible to sell goods or services.
- Compiling these costs helps organizations mensurate profitability and related numbers, like operating turn a profit margin.
- Past keeping a close heart on operating expenses, finance teams can identify outliers and trends that could reveal opportunities to reduce expenses without sacrificing product or service quality.
- Accounting software makes it much easier to summate and rail operating expenses and related metrics.
Operating Expense Explained
Having a clear picture of OpEx, COGS and non-OpEx is crucial to figuring out whether your business is assisting. There is no difficult-and-fast rule on the ideal per centum of operating costs relative to revenue. It will differ depending on the business organisation model, industry and the business organisation'southward maturity. Only equally a general rule, keeping operating costs nether control and selling more of your products or services creates more free cash period for the concern, which is a expert thing.
What Are Operational Activities?
Operating costs are the upshot of a company's operating activities, or activities directly related to selling products or services to customers. Employee travel, marketing campaigns and repair of key equipment are all examples of operational activities.
On the greenbacks flow statement, operating cash menstruation measures the cash coming into and out of the business from these operating activities. Greenbacks comes in, for example, from the sale of goods or services, and greenbacks flows out to pay employees. Other classifications on the cash flow statement, like investing and financing activities, are considered non-OpEx.
What Is Included in Operating Expenses?
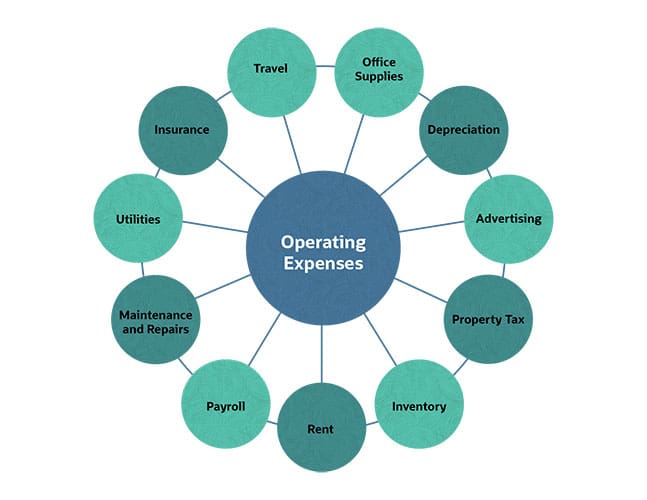
Operating costs, which include many of the expenses necessary to keep a business on its feet, consist of a wide array of expense categories. Here are 11 examples of these expenditures, which are related to various areas of a business'southward core operations:
-
Office Supplies. These are items that are consistently used by office staff or crave regular replenishment such as printer paper, invoices and sales receipts, staplers, pens, janitorial cleaning supplies and USB flash drives.
-
Depreciation. This refers to stock-still assets bought by a company that depreciate in value over time. Assets that depreciate include warehouse equipment and machinery, furniture, computer equipment, delivery vehicles, buildings and shop displays.
-
Advertising. Advertising includes any money spent on marketing the company. For example, business cards, social media, brochures, websites, and TV, print and digital campaigns.
-
Holding Tax. These are real estate taxes that vary based on the assessed value of a belongings.
-
Inventory. Any expenses related to ordering and storing inventory in preparation for auction fall under operating expenses. For example, transportation and delivery, raw materials, manufacturing overhead, storage and labor costs are all inventory expenses.
-
Hire. This includes any costs associated with utilizing a location or property, unowned by business, for factory, storage, office or retail infinite. Within the real manor manufacture, the operating expense ratio (OER) is a metric used to compare the costs associated with operating properties with the revenue that said backdrop generate. Lower OERs are preferable and indicators of increased profitability equally they propose that less of the belongings's income is going toward OpEx.
-
Payroll. Any administrative expenses related to employee wages, benefits and payroll taxes are part of OpEx.
-
Maintenance and Repairs. This refers to all necessary and unavoidable upkeep expenses incurred to keep items in working lodge. This includes fixing and replacing cleaved equipment items, painting and the costs of cleaning and inspecting business structures.
-
Utilities. Utilities include concern expenses from public services such as water, electricity, internet, phone, sewage, heating and waste material disposal.
-
Insurance. This is the coin businesses pay to purchase an insurance contract and the monthly unpaid premium costs associated with said contract.
-
Travel. Travel expenses incurred by a company that become toward reimbursing all business-related travels are function of OpEx.
Importance of Operating Expenses
Operating expenses are necessary to run any business. But, if they exceed the company's total revenue, the company will not make any profit. With that in mind, costs associated with people, energy, transportation and travel are 4 types of operating expenditures companies tin examine for cost-saving opportunities when they have a clear view of these expenditures.
How to Calculate Operating Expenses
Operating costs vary from i organization to another. Some companies have expenses that others don't accept to worry nearly, simply due to the nature of their business. Keeping that in mind, here'south a general formula for calculating operating costs:
Operating Expenses = Payroll/Wages + Sales Commissions + Marketing/Advertising Costs + Rent + Utilities + Insurance + Taxes
Businesses can then use their OpEx, COGS and non-OpEx to measure turn a profit. Get-go with this elementary formula from the U.S. Small Business Assistants:
Sales – Cost of Appurtenances Sold = Gross Profit – Overhead = Net Profit
While that formula is pretty straightforward, it's not e'er immediately obvious whether, for case, a transportation-related toll should be placed under COGS or OpEx.
COGS for a manufacturer, for instance, includes every toll associated with buying materials, freight costs to go those supplies to your warehouse or plant, expenses to make the product, modifications and packaging. That number is subtracted from the catastrophe inventory to arrive at the COGS. (Note that IFRS and U.Southward. GAAP accounting standards use different methods to go COGS.)
The side by side step is to decrease COGS from sales to become the gross profit. This is where OpEx come into play. Once a company subtracts operating expenses from gross profit, it has its net turn a profit.
Example of Operating Expenses
Take the water ice cream shop Dig Dog Water ice Cream as a elementary example of this calculation. Dig Dog sells $200,000 worth of ice cream annually. The COGS includes the cones, ice cream and paper wrappers minus all of the supplies that weren't used, amounting to $75,000. Operating costs include $ii,000 in utilities, $10,000 in rent, $40,000 in salaries, $ane,000 depreciation of the freezer and $2,000 for business insurance. There are no non-operating costs. That would brand its net profit $seventy,000. (Come across the adding below.)
$200,000 – $75,000 (COGS) = $125,000 (gross profit) – $55,000 (overhead) = $lxx,000 (cyberspace profit)
Operating Expenses on an Income Statement
Below is an income statement template provided by the U.S. Modest Business Administration with a detailed list of many common operating expenses. (Come across highlighted department.)
This automated form is made available compliments of CCH Business Owner'south Toolkit
| [Your Company Name] Income Statement For the Year Ended [MM, DD, YYYY] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue: | ||||||
| Gross Sales | $0.00 | |||||
| Less: | Sales Returns and Allowances | $0.00 | ||||
| Cyberspace Sales | $0.00 | |||||
| Cost of Appurtenances Sold: | ||||||
| Kickoff Inventory | $0.00 | |||||
| Add: | Purchases | $0.00 | ||||
| Freight-in | $0.00 | |||||
| Directly Labor | $0.00 | |||||
| Indirect Expenses | $0.00 | |||||
| $0.00 | ||||||
| Less: | Ending Inventory | $0.00 | ||||
| Cost of Goods Sold | $0.00 | |||||
| Gross Profit (Loss) | $0.00 | |||||
| Expenses: | ||||||
| Advertising | $0.00 | |||||
| Amortization | $0.00 | |||||
| Bad Debts | $0.00 | |||||
| Bank Charges | $0.00 | |||||
| Charitable Contributions | $0.00 | |||||
| Commissions | $0.00 | |||||
| Contract Labor | $0.00 | |||||
| Credit Bill of fare Fees | $0.00 | |||||
| Delivery Expenses | $0.00 | |||||
| Depreciation | $0.00 | |||||
| Dues and Subscriptions | $0.00 | |||||
| Insurance | $0.00 | |||||
| Interest | $0.00 | |||||
| Maintenance | $0.00 | |||||
| Miscellaneous | $0.00 | |||||
| Office Expenses | $0.00 | |||||
| Operating Supplies | $0.00 | |||||
| Payroll Taxes | $0.00 | |||||
| Permits and Licenses | $0.00 | |||||
| Postage stamp | $0.00 | |||||
| Professional Fees | $0.00 | |||||
| Property Taxes | $0.00 | |||||
| Rent | $0.00 | |||||
| Repairs | $0.00 | |||||
| Phone | $0.00 | |||||
| Travel | $0.00 | |||||
| Utilities | $0.00 | |||||
| Vehicle Expenses | $0.00 | |||||
| Wages | $0.00 | |||||
| Full Expenses | $0.00 | |||||
| Net Operating Income | $0.00 | |||||
| Other Income: (not-operating expenses) | ||||||
| Proceeds (Loss) on Sale of Assets | $0.00 | |||||
| Interest Income | $0.00 | |||||
| Total Other Income | $0.00 | |||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $0.00 | |||||
How to Utilise Operating Expenses
Knowing the total amount of operating costs helps businesses calculate turn a profit and another valuable number: operating income, which is also referred to equally earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT). How operating income changes over fourth dimension will assist businesses and potential investors determine whether it'south an efficient operation.
Operating Income = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
Once a business knows its OpEx, it tin can use more complex formulas that lend insight into overall profitability, such as operating profit margin.
Operating Profit Margin = EBIT / Sales Revenue x 100
The higher the operating profit margin percentage, the more profitable the business.
What's more, increasing sales without a significant increase in operating costs is crucial to growing profits. That's why understanding OpEx is helpful, as finance teams tin drill into expense line items to see outliers and trends and then look for ways to reign those in.
How to Cut Operating Costs
Research suggests that a 1% decrease in operating costs can increase profitability upward to x times more than a corresponding increment in revenue, per Capgemini. With a articulate view of operating costs, you tin place areas that appear too costly, then break out and examine them to detect opportunities for cost savings.
Here are a few common ways to reduce operating expenses:
- Review utility bills — accept they gone upwards over fourth dimension? Look for energy-efficient investments, such as motility-sensor lights or HVAC upgrades.
- Evaluate options for cyberspace/cable and insurance providers. See if another vendor offers a more competitive price.
How Accounting Software Helps Calculate Operating Expenses
To automate the process of tracking, recording and classifying expenses, most businesses plow to bookkeeping software. The first step in the U.S. Small Business organisation Assistants's list of "X Basic Bookkeeping Steps" is to buy accounting software, which is ahead of opening a dissever concern checking account, reconciling that account and even tracking sales.
Bookkeeping and financial direction software are essential for monitoring revenue and expenses, generating financial reports and tracking other metrics that ensure the financial wellness of the business. Automation reduces errors borne of manual data entry and makes a time-consuming process much more efficient.
Above all, such a organisation will aid a business generate accurate financial statements and reports that comply with U.S. GAAP and IFRS accounting standards.
Operating expenses are a gold mine of data that businesses can examine to reduce costs and bulldoze efficiency beyond their organization. One time companies realize the sheer value of securely analyzing and organizing their operational expenses, they can work toward reducing them while maintaining product prices and quality and increasing profitability.
Operating Expenses FAQs
What is included in the operating expenses?
Operating expenses are any costs incurred through daily business activities that don't fall nether cost of appurtenances sold. Variable operating expenses, such as packaging or shipping costs, fluctuate depending on the volume of an activity or the occupancy rate of a property. Conversely, fixed operating expenses, such equally salaries or mortgage payments, remain consistent, equally they are non influenced by book or occupancy.
What are examples of operating expenses?
Mutual operating expenses for a company include hire, payroll, travel, utilities, insurance, maintenance and repairs, property taxes, office supplies, depreciation and advertising.
What are the categories of operating expenses?
Operating expenses can be broken down into 3 categories: office, compensation and sales- and marketing-related expenses. Part-related expenses come from typical office settings, and often include things like office supplies, property taxes, rent and insurance. Bounty-related expenses consist of payroll, employee benefits, sales commissions and pension plans. Finally, marketing- and sales-related expenses are directed toward all advert materials, travel and entertainment.
What is not included in operating expenses?
Not-operating expenses are incurred exterior of everyday business organization activities and related to financing or investing activities. Examples of not-operating costs include obsolete inventory charges, lawsuit settlements, losses on investments, damages caused by natural disasters and fires, restructuring costs and involvement expenses. Any costs related to making goods or delivering services are also non role of OpEx.
What Is A Good Operating Expense Ratio For A Hvac Service Co,
Source: https://www.netsuite.com/portal/resource/articles/financial-management/operating-expense.shtml
Posted by: meyersnobbland.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is A Good Operating Expense Ratio For A Hvac Service Co"
Post a Comment